Science 101: Understanding pH
What is pH?
First of all, it is important to understand what pH means. The letters pH stand for potential hydrogen. It is a value used to express the acidity or alkalinity of a chemical solution.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. The smaller the number, the higher the acidity; the higher the number, the more alkaline, or basic, the substance is. Anything below 7 is acidic, and anything above 7 is basic. Alkalis are a subclass of bases, so we also use the term basic solution to describe an alkaline solution. Solutions with a pH of 7 are neutral.
Here are some examples of pH values for a few common solutions:
- Lemon juice = pH of 2.5
- Beer = pH of 4.5
- Pure water = pH of 7
- Blood = pH of 7.4
- Soap = pH of 9.5
- Ammonia = pH of 11
- Bleach = pH of 11.5
- Laundry detergent = pH of 13
The pH is a logarithmic scale
The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning that if the pH of a solution decreases by one unit, the solution becomes ten times more acidic. If its pH decreases by two units, the solution becomes 100 times more acidic. It is also important to note that the pH of a concentrate is different from the pH of a solution diluted with water. This is why cleaning chemicals should NEVER be mixed together, especially those at either end of the pH scale as dangerous chemical reactions may occur. Mixing could also neutralize products, rendering them completely ineffective.
The role of pH in cleaning products
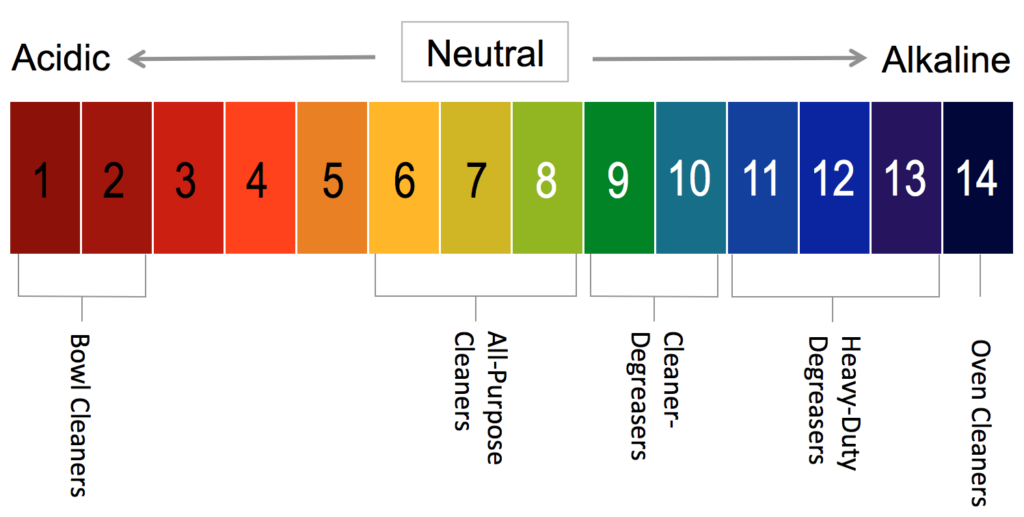
The first thing to keep in mind is that products with an acidic pH remove substances of mineral origin (descalers, scrubs), and those with a basic pH remove substances of organic origin (degreasers, strippers).
Acidic cleaners
Acidic cleaners are especially effective on specific soils such as scale, calcium, oxidation caused by water or air, juice, coffee, rust, and hard water mineral build-up. These products must be used with care due to their high acidity level, which can sometimes damage surfaces or alter colours. Acidic cleaners have a pH value of between 0 and 7.
Bowl, porcelain and ceramic cleaner
Descalers are acidic products that remove mineral deposits from surfaces such as porcelain, and are used primarily to clean toilet bowls. Due to the significant risks associated with the use of acidic solutions (health and safety, damage to materials, etc.), it is recommended to exercise caution when using these.
Recommendations for acidic cleaners:
- Bowl, urinal and porcelain cleaner, INO bano 7 (pH 2)
- Scrub-free cleaner for soap scum and scale residues, INO bio 10 (pH 3-4)
- Washroom cleaner, INO bano 11 (pH 4)
SaniDépôt also stocks INO bano 1, Daily use Elite washroom cleaner, (Acid-Free), pH 6-8.
Neutral products
Neutral cleaners are used on more delicate surfaces, such as waxed floors and countertops, to avoid damaging them.Acidic or alkaline cleaners can dull or damage a floor finish and cause it to deteriorate more quickly. Neutral cleaners have a pH value between 6 and 8.
Neutral detergents (or all-purpose cleaners)
Neutral detergents, commonly referred to as all-purpose or multi-purpose cleaners, have a pH ranging from 5 to 9, allowing them to remove dirt without damaging finishes. They can be used daily on a variety of surfaces including office furniture and floors.
Recommendations for all-purpose cleaners:
- All purpose cleaner, INO bio 1 (pH neutral)
- Neutral floor cleaner, INO gloss 12 (pH 7)
Alkaline cleaners
Alkaline cleaners are highly effective on the toughest dirt and heavily soiled areas.
Glass cleaners
Because they contain a fast-evaporating agent (alcohol, ammonia, etc.), glass cleaners must be diluted correctly to avoid leaving streaks. The most effective glass cleaners are formulated with a pH of between 8 and 11, which allows them to clean even heavily soiled windows without causing damage to frames.
Recommendations for glass cleaners:
- Glass and window cleaner, INO Kleen 3 (pH 10.5-11.5)
- Concentred glass cleaner, INO Kleen 8 (pH 11)
Degreasing detergents
Degreasers have a more basic pH than neutral detergents, which makes them effective in removing tougher dirt such as grease or hydrocarbon-based oil, etc. In addition, some degreasing detergents are derived from biotechnology (enzymatic compounds) that target specific types of matter such as food grease and oil.
Recommendations for degreasers:
- Concentrated degreaser, INO Kleen 7 (pH 12)
- Degreaser deodorant elite cleaner, INO chef 2 : A powerful, non-butyl degreaser formulated to remove all hydrocarbon-, animal- and vegetable-based oils and greases. The product is an optimal blend of the most advanced wetting agents and emulsifiers. It is extremely versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications.
- Degreaser for kitchen floors, INO bio 8 : Cleans floors effectively and leaves them much less slippery. It is formulated to leave a bio-film that continues to biodegrade fats and helps to eliminate odours even after cleaning.
Dishwasher detergents (alkaline pH)
Dishwasher detergents are alkaline solutions that are excellent for cleaning dishes and encrusted organic matter but are generally not very effective at removing minerals from water (e.g., hard municipal water, which contains minerals such as iron, calcium, magnesium, etc.). For this reason, dishwashers should be treated regularly with an acidic product to remove mineral build-up.
The INO chef 60 descaler removes calcium deposits and scale. It is also safe for stainless steel, china or glassware when used as directed.
Recommendations for dishwasher detergents:
- Mechanical warewashing detergent, INO chef 15 (High temperature)
- Mechanical warewashing detergent, INO chef 19 (Low temperature)
Recommendations for dishwasher descaling products:
Where to find a product’s pH?
A product’s pH can be found in the description of its physical and chemical characteristics. This information appears on the product label or in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS). SDSs “are summary documents that provide information about the hazards of a product and advice about safety precautions.” (Source: CCOHS, Government of Canada)
Conclusion
Selecting the right product, ensuring the proper dilution with water and employing the appropriate cleaning method all play a key role in effective cleaning. It is also important to remember that cleaning products can pose a danger for users, the occupants of the premises and the environment, both in the workplace and at home. That’s why when it comes to choosing a product, it is essential to consider its ingredients, how it works and its primary function.


